10 major facts about the monkeypox virus
- Monkeyopox is a rare disease that occurs primarily in remote parts of Central and West Africa, near tropical rain forests
- Its outbreak in Bayelsa state has caused panic in Nigeria
- Legit.ng lists 10 major facts about the disease everyone should know
Residents of Bayelsa state have been gripped by fear following after the outbreak of a rare deadly viral disease known as Monkey Pox in the state.
The state commissioner for health, Professor Ebitimitula Etebu, has since confirmed the development.
Monkeypox is a rare disease that occurs primarily in remote parts of Central and West Africa, near tropical rain forests.
READ ALSO: Osinbajo challenges government at all levels on synergy to meet water supply, sanitation demands
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention has listed the major facts about the disease.
Legit.ng lists the facts below:
1. Double stranded DNA virus (Zoonotic)
Family poxviridae, Genus orthopoxvirus
Family of pox viruses includes other viruses like chicken pox or the eradicated small pox.
2. History
1958: First identified in laboratory monkey kept for research
1970: First human case was identified in DR Congo
1985: First isolation in nature, in an ailing rope squirrel in DR Congo
2003: First human infection outside Africa documented in USA
3. Transmission
From infected animals or humans
Following contact with body fluids/materials of animals or infected humans
Following bite, scratch or even bush meat preparation
Entry via broken skin or mucosa (skin, respiratory tract, mucus membrane eye, nose, mouth).
Shared utensils, bed, room etc increase risk of transmission
4. Incubation period
7-14 days commonly but could extend from 5 to 21 days.
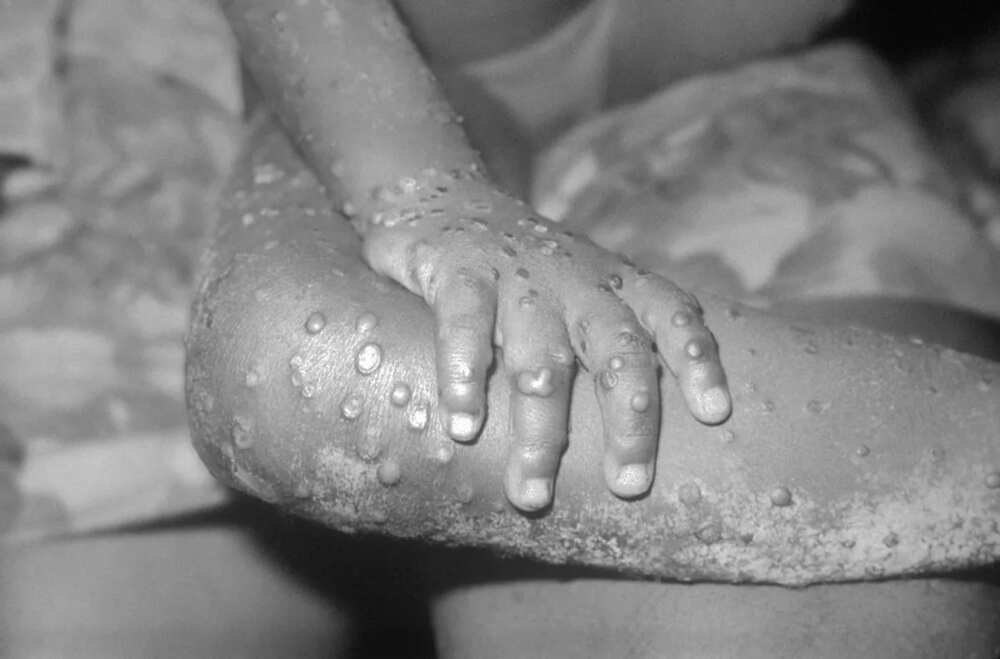
5. Signs and symptoms
Similar to small pox but milder
Fever, chills, drenching night sweats, headache
Muscles aches (backache), Exhaustion-Lymph-nodes swell up (absent in small pox)
6. Case definition
A: Designed to detect single cases followed by immediate response and control efforts.
- Fever followed by rash (vesicular/pustular) with rash on palm, soles and face or 5 various-like scars
B: Designed for use in the context of disease surveillance to elaborate on burden in endemic areas
- Individual with vesicular/pustular eruptions with at least one of the symptoms: fever preceding eruptions, lymphadenopathy and/or pustules/crust on the palms of the hands or sole of the feet
7. After 1-10 days
Centrifugal rash: Rash macule-papule-vesicles-pustules-umbilical-then crusted (scab)
8. Case fatality
-1-10% die from this infection
9. Prevention
Small pox vaccine (for at risk workers) which can be given up to 14 days post exposure
Hygiene (Hand washing) with soap and water or alcohol based sanitizer
Avoid ill or dead animals’ suspects or their materials
Isolation of suspects or identified cases
Use personal protective equipment when caring for patients (for health workers)
10. Treatment and vaccine
There are no specific treatments or vaccines available for monkeypox infection, but outbreaks can be controlled. Vaccination against smallpox has been proven to be 85% effective in preventing monkeypox in the past but the vaccine is no longer available to the general public after it was discontinued following global smallpox eradication.
READ ALSO: 3 million children need emergency education support in Borno - UNICEF
Nigerians speak out against N1500 budget for health per person - Legit.ng TV
Source: Legit.ng
